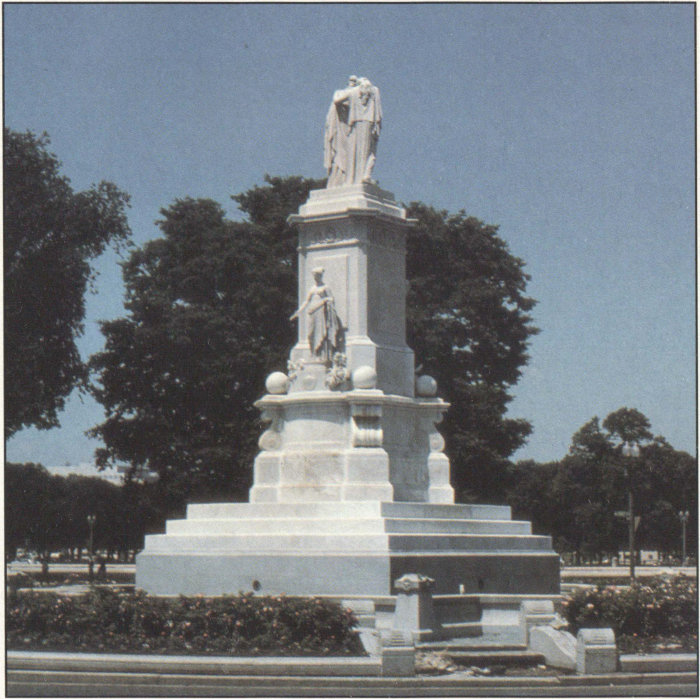
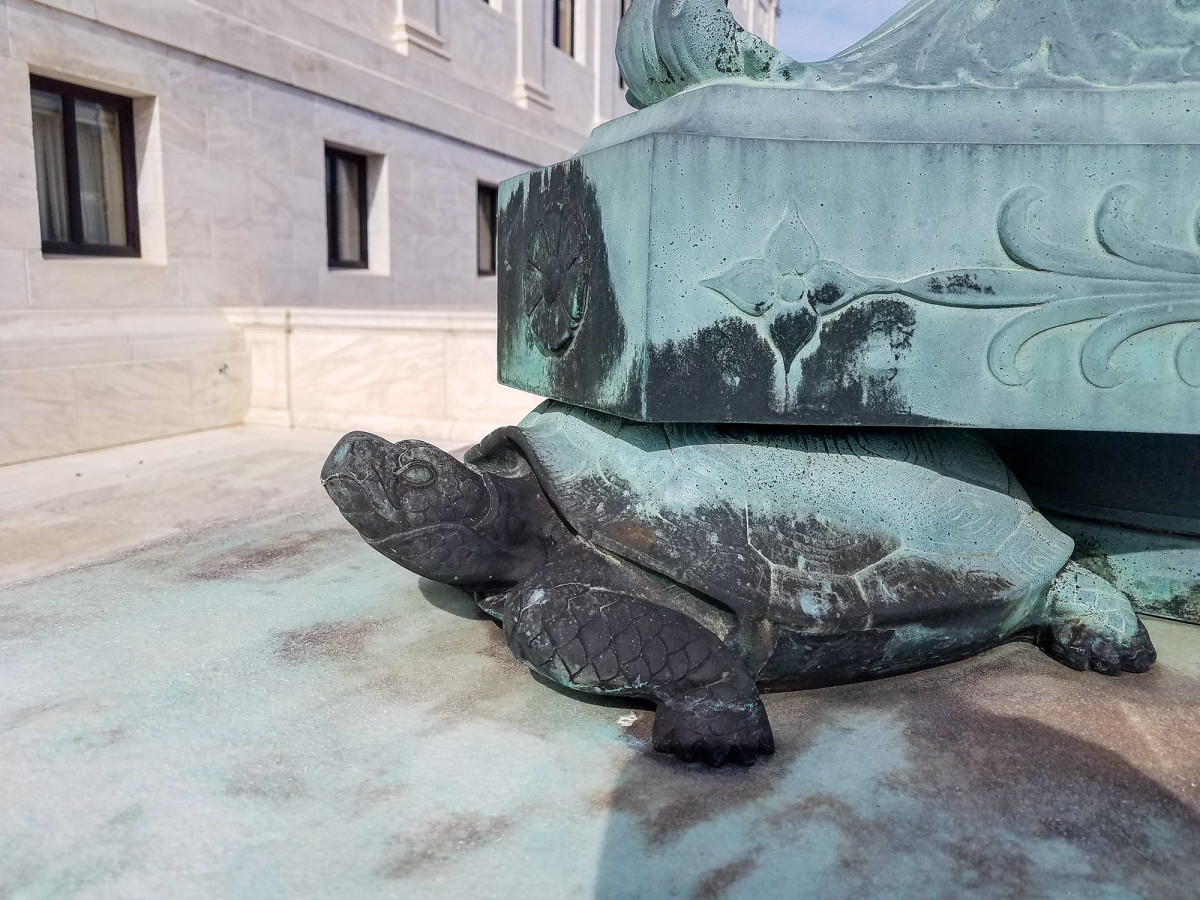
Many monuments are made from limestone marble and bronze materials that can be altered or slowly dissolved by acid precipitation.
Why does acid rain dissolve statues made of marble.
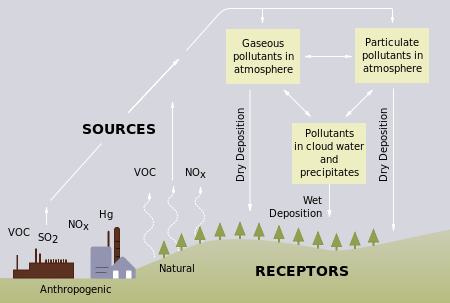
Acid precipitation affects stone primarily in two ways.
The marble has caco as the major component.
The acids in acid rains can react with caco by producing soluble salts.
Not only does acid rain aggressively dissolve calcium in stone but it corrodes certain types of metal.
Caco3 s h2so4 aq caso4 aq co2 g h2o l caso4 is pretty insoluble stuff but it will dissolve in the large amount of water during the process of the degradation of the caco3 caused by acid rain.
When sulfurous sulfuric and nitric acids in polluted air react with the calcite in marble and limestone the calcite dissolves.
Vulnerable metals include bronze copper nickel zinc and certain types of steel.
That s why acid rain dissolves statues made of marble.
The reaction between caco and h so acid is caco s h so aq caso aq co g h o l caso is slightly soluble in water.
In exposed areas of buildings and statues we see roughened surfaces removal of material and loss of carved details.
No one expects the washington monument to melt into a toothpick but acid rain damage may slowly add up for our beloved icons.
A study in the journal water air and soil pollution by the university of hong kong reported that artificial acid rain with a ph of 3 5 could corrode.
Slowly is the key word of course.
When sulfurous sulfuric and nitric acids in polluted air and rain react with the calcite in marble and limestone the calcite dissolves.